How Fast Charging Cables Really Work Explained
Fast charging cables* have become an essential part of modern life. Whether you’re powering up your smartphone, tablet, or laptop, the need for speed is real. But have you ever wondered how these cables work their magic? It’s not just about pumping more power it’s a careful balance of voltage, current, cable construction, and communication protocols.
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about how fast charging cables actually work. From core components to key technologies, we’ll help you understand what’s really happening when your battery percentage climbs rapidly.
Understanding the Basics of Charging
To get a grasp on fast charging, we first need to understand standard charging. In its simplest form, charging involves transferring electrical energy from a power source (like a wall adapter) to your device’s battery.
The speed at which this happens depends on two main things:
- Voltage (V): The force pushing the electricity.
- Current (A): The volume of electricity being pushed.
In regular USB charging, the power output is usually 5 volts and 1 amp, which equals 5 watts of power. But fast charging increases either the voltage, the current, or both.
The Science Behind Fast Charging
Fast charging is essentially about delivering more power to your device in a shorter time. This is achieved by increasing the voltage or current, sometimes both. Here’s the basic power formula:
Power (W) = Voltage (V) × Current (A)
So, a fast charger delivering 9V at 2A will output 18W of power much faster than the standard 5W.
There are different fast charging technologies like:
- Qualcomm Quick Charge
- USB Power Delivery (USB-PD)
- OPPO VOOC / OnePlus Dash
- Samsung Adaptive Fast Charging
Each of these standards operates differently, but the idea is the same: safely send more power, more quickly.
What Makes a Cable “Fast Charging”
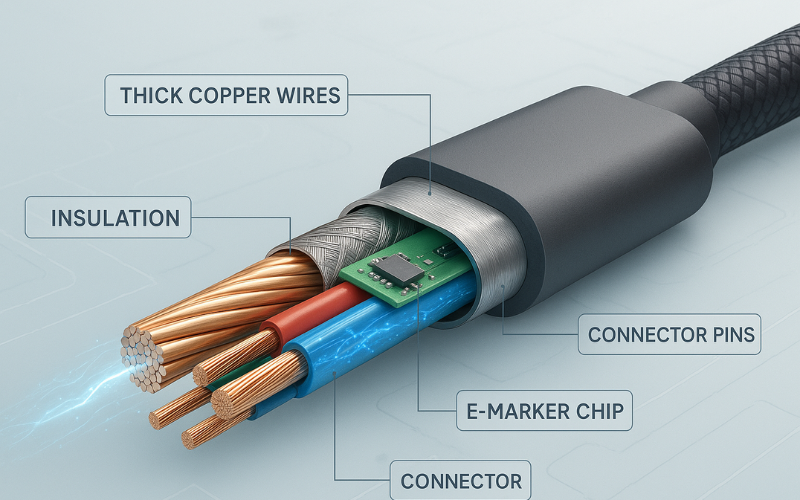
The cable is just as important as the charger itself. A fast charging cable is designed to handle higher power transmission without overheating or degrading. Here are the main components that make a difference:
1. Wire gauge (thickness):
Fast charging cables use thicker wires usually 24AWG or lower for power lines. Thicker wires reduce resistance and allow more current to pass.
2. Cable shielding and materials:
High-quality shielding reduces electromagnetic interference. Materials like braided nylon or TPE also impact durability and performance.
3. Connector quality:
Gold-plated or reinforced connectors offer better contact and less power loss.

Let’s take a quick comparison:
| Feature | Standard Cable | Fast Charging Cable |
| Wire Gauge | 28AWG (thinner) | 24AWG or thicker |
| Max Current | Up to 1A | Up to 3A or higher |
| Shielding | Basic | Multi-layered |
| Data Transfer | USB 2.0 (480 Mbps) | USB 3.0/3.1 (up to 10 Gbps) |
| Connector Durability | Standard | Reinforced or gold-plated |
Smart Chips and Communication Protocols
Fast charging isn’t just brute force there’s a smart communication process happening between your phone and the charger. Inside most modern cables and chargers is a chip that communicates with your device to negotiate:
- Voltage level
- Current requirement
- Charging speed limitations
For example, USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) uses a smart handshake process that allows the charger to “talk” to your device and determine the optimal power output. This prevents overheating or battery damage.
These smart chips also enable features like:
- Trickle charging at 100%
- Temperature control
- Adaptive power delivery
Types of Fast Charging Connectors
Different devices use different types of connectors, and that can impact charging speeds. Here are the most common ones:
USB-A to Micro USB:
Outdated for fast charging. Supports up to 2.4A but lacks communication protocols.
USB-A to USB-C:
Widely used today. Can support up to 3A current with fast charging compatibility if paired with proper adapters.
USB-C to USB-C:
The gold standard for fast charging. Supports USB-PD and allows for up to 100W of power delivery.
Lightning Cables (Apple):
Support fast charging with USB-C to Lightning cables when paired with an 18W or higher adapter.
Here’s a quick table for comparison:
| Connector Type | Max Power Supported | Fast Charging Compatible |
| USB-A to Micro USB | 12W | Limited |
| USB-A to USB-C | 15–18W | Yes |
| USB-C to USB-C | 100W | Yes |
| USB-C to Lightning | 30W+ | Yes |
Why Not All Fast Charging Cables Work the Same
Just because a cable looks like a fast charger doesn’t mean it is. Many cheaper cables don’t have the internal components needed for high-speed charging.
Look out for these signs of a poor-quality cable:
- It feels unusually light or thin
- Charging takes longer even with a fast charger
- It heats up during use
- It doesn’t support data transfer or is unstable
When shopping for fast charging cables, look for these labels:
- “Supports up to 3A current”
- “USB-IF certified”
- “Compatible with Quick Charge or USB-PD”
- “E-Marker chip included” (for USB-C cables)
How to Test If a Cable Supports Fast Charging
Want to know if your cable is truly fast charging? Here’s how you can check:
1. Use a USB power meter:
These small devices plug between your charger and device to show real-time voltage and current.
2. Look at charging times:
If your phone supports fast charging and the cable is legitimate, you’ll usually reach 50% in around 30 minutes.
3. Check your phone settings:
Some Android phones display “Fast Charging” or “Quick Charging” when connected to the right combo of cable and charger.
4. Use certified apps:
Apps like Ampere or AccuBattery can estimate the charging rate and help diagnose weak cables.
Tips to Choose the Best Fast Charging Cable
To make sure you’re getting the best value and safety, here are key tips:
- Check compatibility: Make sure the cable supports your device’s charging protocol.
- Length matters: Longer cables often reduce power delivery slightly. Keep it under 1.5m for optimal speed.
- Go branded or certified: Anker, Aukey, Belkin, and Baseus are reliable brands with solid warranties.
- E-Marker Chip for USB-C: This chip ensures your cable can safely handle high wattage (e.g., for laptops or tablets).
Bonus Tip:
Avoid charging your phone with your laptop’s USB-A port. It delivers low power and won’t trigger fast charging.
Fast Charging Is a Team Effort
Fast charging isn’t just about one powerful cable. It’s a coordinated system involving:
- A high-power adapter
- A high-quality cable
- A device that supports fast charging protocols
- Smart communication chips
When all these work together, your device gets charged faster, more efficiently, and safely.
If you want the best performance, don’t just focus on the wall adapter invest in the right cable too. It’s the hidden hero in your charging setup.
Leave a reply